In today's world, where consumers care more about the environment, eco certifications have become key. These labels show that products meet strict environmental and ethical standards. For business owners, knowing the criteria behind these labels can boost your brand and help you run a more sustainable operation.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is a big part of any good eco certification. It looks at the environmental effects of a product throughout its life—from getting raw materials to making, distributing, using, and disposing of it.
1. Life Cycle Analysis (LCA)
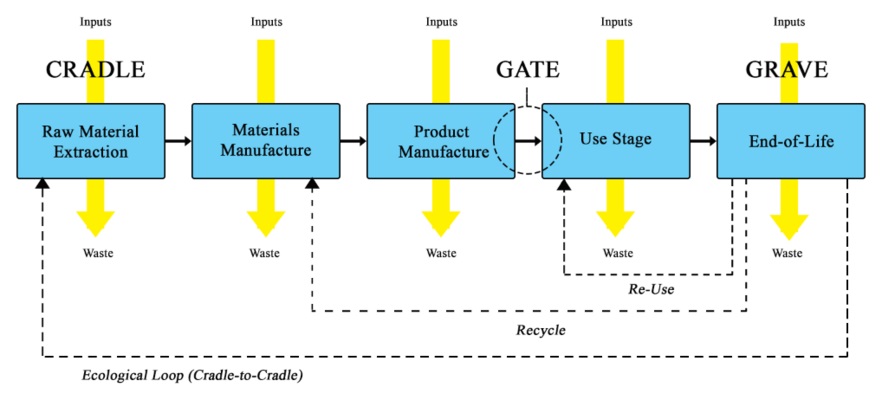
Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) checks the environmental impact at every stage of a product's life. This analysis helps businesses find ways to be more sustainable. For example, switching to renewable energy sources during manufacturing can significantly reduce your carbon footprint. A company like Patagonia, for instance, uses LCA to assess its products, ensuring they are made with minimal environmental impact.
2. Resource Efficiency

Eco certifications focus on using resources efficiently. This includes cutting down on water, energy, and raw materials. Businesses are encouraged to use sustainable materials, like recycled content, to save natural resources. For instance, bamboo is often chosen over traditional hardwood because it grows quickly and renews itself. An example is IKEA's commitment to using only sustainable cotton and recycled materials in its products by 2030.
3. Emission and Waste Management
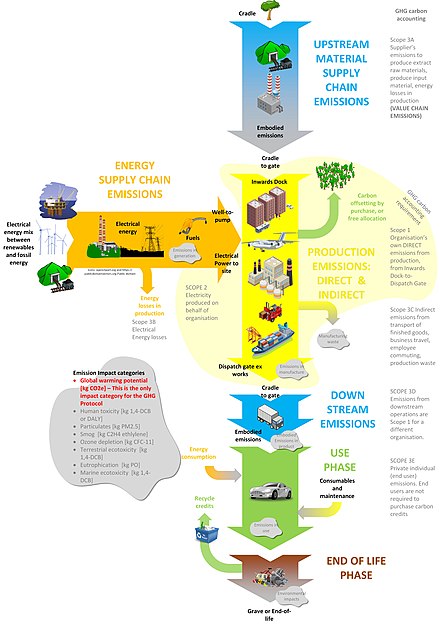
Lowering emissions and managing waste are crucial. Products that generate fewer greenhouse gasses, toxic chemicals, or non-biodegradable waste are preferred. Eco certifications often require companies to start recycling programs, waste reduction initiatives, and advanced pollution control measures. For example, the tech company Apple has programs to recycle old devices and aims to make products using only recycled or renewable materials.
4. Biodiversity Preservation

Eco certifications also care about preserving biodiversity. Products from ecologically sensitive areas, like rainforests, are checked to ensure they don't harm habitats or endanger species. Certifications might promote sustainable farming practices that support biodiversity while benefiting local communities. For example, the Rainforest Alliance certification ensures that products like coffee and chocolate are sourced from farms that protect wildlife habitats.
Social and Ethical Considerations
Eco certifications also look at social and ethical aspects. This means eco-friendly products should contribute positively to society and respect human rights.
1. Fair Labor Practices

Certifications often require fair labor practices. This means fair wages, safe working conditions, and respect for workers' rights. Meeting these standards helps fight issues like child labor, exploitation, and unsafe work environments, promoting a fairer workplace. Companies like Fairphone focus on creating electronics that adhere to fair labor practices, ensuring workers are treated ethically throughout the supply chain.
2. Community Engagement

How production affects local communities is also important. Certifications check if companies help local economies and don't deplete resources or displace communities. Businesses that invest in community development—like funding education or healthcare—are highly valued. An example is TOMS shoes, which donates a pair of shoes to a child in need for every pair sold, significantly impacting community welfare.
3. Ethical Sourcing
Ethical sourcing ensures raw materials are obtained in a way that respects both people and the environment. This often means supporting small farmers or indigenous communities, ensuring they get fair prices and their rights are protected. Certifications like Fair Trade show a commitment to ethical sourcing. Ben & Jerry's, for instance, sources Fair Trade-certified ingredients for their ice creams, ensuring farmers are fairly compensated.
4. Animal Welfare

For products with animal ingredients, certifications check how animals are treated. Standards might include humane treatment, good living conditions, and avoiding unnecessary suffering. For example, cosmetics certifications often require cruelty-free testing methods, ensuring no harm to animals during product development. Brands like Lush are known for their strict cruelty-free policies and use of ethical ingredients.
Transparency and Traceability
Transparency and traceability are key for keeping eco certifications credible. They assure consumers that products meet the promised environmental and ethical standards.
1. Supply Chain Transparency
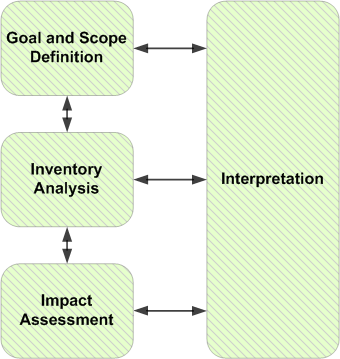
A transparent supply chain shows where and how a product is made. This helps verify that every step meets eco-friendly criteria. Businesses must track raw materials from their source to the final product, ensuring compliance with standards. This level of transparency builds trust and accountability. For instance, companies like Unilever provide detailed information about the sourcing and production processes of their products.
2. Credible Certification Bodies


Third-party certification bodies are crucial for maintaining the integrity of eco labels. These organizations set high standards and conduct thorough audits to ensure compliance. Trusted certifications from bodies like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) are well-respected because of their strict assessment processes. These bodies ensure that certified products genuinely meet high environmental and social standards.
3. Public Reporting and Accountability
Eco certifications often require businesses to publicly report their environmental and social performance. This allows consumers to see the real impact of their purchases and holds companies accountable. Regular reporting shows a company's ongoing commitment to sustainability. Patagonia, for example, publishes detailed reports on its environmental impact and the steps it takes to improve.
4. Consumer Education
Educating consumers about what certifications mean and how products achieve them is important. This transparency helps consumers make informed choices and supports companies truly committed to sustainable practices. Certifications often come with educational campaigns to help consumers understand the value of eco-friendly products. For instance, the Fair Trade organization runs awareness campaigns to inform consumers about the benefits of Fair Trade products.
The Future of Eco Certifications and Emerging Trends
As sustainability becomes more crucial, the future of eco certifications will evolve with new trends and technologies. Here are some key developments to watch:
1. Technological Advances
Technology will play a significant role in enhancing the transparency and effectiveness of eco certifications. Blockchain, for example, can be used to create immutable records of a product’s journey through the supply chain, ensuring every step is verifiable and transparent.
2. Integration of AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) can help in monitoring and analyzing environmental impacts more accurately and efficiently. AI can process vast amounts of data to identify areas for improvement, predict future impacts, and suggest sustainable alternatives.
3. Consumer Demand and Legislation

As consumer awareness grows, demand for certified eco-friendly products will continue to rise. Additionally, stricter environmental regulations and legislation will push more companies to adopt sustainable practices and seek eco certifications.
4. Expansion of Certification Criteria
Future certifications may expand their criteria to include broader sustainability metrics such as carbon footprint, water usage, and social equity impacts. This holistic approach will ensure products are not only eco-friendly but also socially responsible.
Summing It Up

Understanding the criteria behind eco certifications is essential for both consumers and business owners. For businesses, these certifications are not just about meeting market demands but about making a real commitment to sustainability and ethical practices. By following strict Environmental Impact Assessments, upholding social and ethical standards, and ensuring transparency and traceability, businesses can contribute to a healthier planet and a fairer society.
As consumers become more eco-conscious, the demand for certified eco-friendly products will keep growing. By understanding and embracing these criteria, businesses can enhance their reputation and drive positive change in their industries. Eco certifications are more than just labels; they represent a commitment to a sustainable future.

